Diagnosis and Treatment of Tongue Cancer
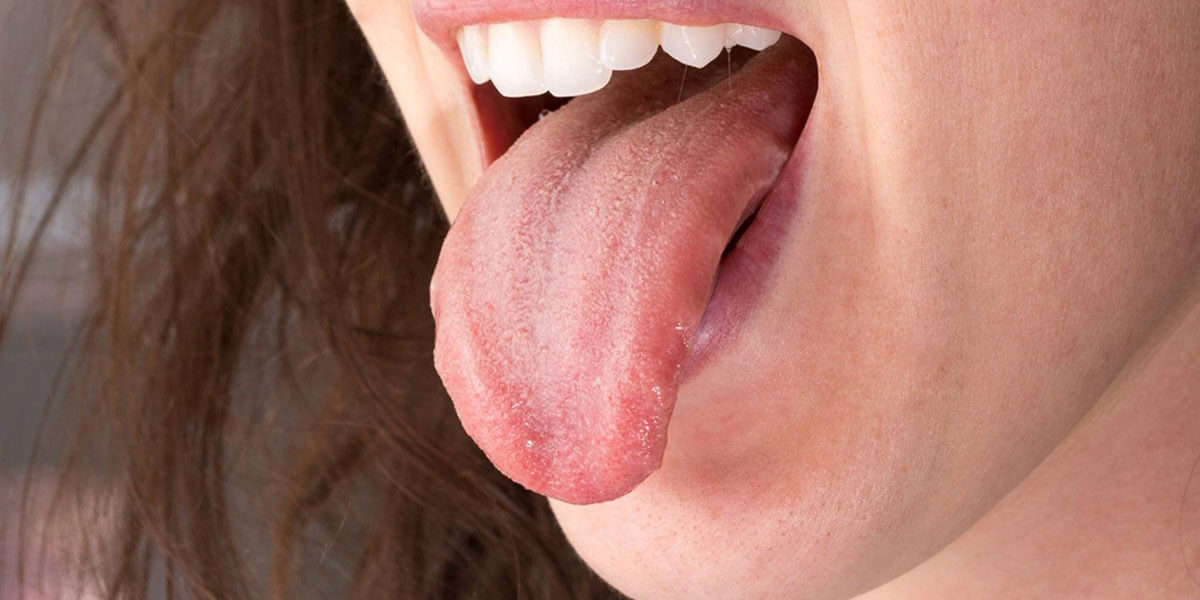
Tongue Cancer: The tongue plays a critical role not only in vital functions such as speech and swallowing, but also in taste perception and overall oral health maintenance. However, in some cases, malignant cellular changes can occur in tongue tissue, leading to the development of tongue cancer. As a significant subset of head and neck cancers, tongue cancer can be successfully managed with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment approaches. At his private clinic in Istanbul, ENT specialist Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen offers his patients high success rates in the diagnosis and treatment of tongue cancer using evidence-based, modern, and individualized methods.
In this article, we will comprehensively cover every detail—what tongue cancer is, why it occurs, which symptoms it presents with, how it is diagnosed, and what treatment options are available.
What Is Tongue Cancer?
Tongue cancer is a malignant tumor formed by the abnormal growth and uncontrolled proliferation of cells in the tongue. The most common histological type is squamous cell carcinoma. Tongue cancer can arise in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue or more posteriorly, near the floor of the mouth.
Cancers that develop on the surface, edges, or underside of the tongue can progress rapidly and metastasize to surrounding tissues, cervical lymph nodes, or, in advanced stages, distant organs. Therefore, early diagnosis is a decisive factor in controlling the disease and achieving treatment success.
Causes and Risk Factors of Tongue Cancer
Several risk factors contribute to the development of tongue cancer. The most common among these are:
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Use of cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and chewing tobacco significantly increases the risk of tongue cancer.
- Alcohol Consumption: Especially in combination with smoking, alcohol use multiplies the risk.
- HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) Infection: HPV is an important risk factor in oral cancers, including tongue cancer.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Dental calculus, ill-fitting dentures, and chronic oral trauma can cause chronic irritation and predispose to cancer.
- Immunosuppression: Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV, increase the risk of tongue cancer.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of head and neck cancers raises individual risk.
Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen carefully evaluates these risk factors, provides preventive recommendations, and implements early screening protocols for at-risk individuals.
What Are the Symptoms of Tongue Cancer?
Early-stage tongue cancer may be asymptomatic or present with mild complaints. Over time, however, the following symptoms may appear:
- Non-healing Sore on the Tongue: Lesions lasting more than two weeks without healing are significant.
- Mass or Swelling on the Tongue: Firm, painless nodules may form on the tongue’s edge, surface, or underside.
- Pain: Pain in the tongue or during swallowing may indicate advanced disease.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Trouble swallowing liquids or solids.
- Bleeding: Unexplained bleeding from the tongue.
- Changes in Taste: Loss of taste or metallic taste sensations.
- Speech Difficulties: Impaired tongue movement resulting in speech disruption.
- Neck Swelling: Painless neck lumps due to lymph node metastasis.
If any of these symptoms are observed, an ENT specialist should be consulted without delay. Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen initiates the early diagnosis process by thoroughly evaluating patient complaints.
How Is Tongue Cancer Diagnosed?
Early and accurate diagnosis is a cornerstone of successful tongue cancer treatment. The diagnostic process progresses through several stages:
- Clinical Examination: A detailed inspection of the oral cavity and tongue; suspicious areas are carefully assessed.
- Endoscopic Evaluation: Flexible endoscopy may be used for more detailed imaging of the mouth and throat.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the suspicious lesion for pathological examination. Biopsy is essential for definitive diagnosis.
- Imaging Studies: MRI, CT, and PET-CT scans determine tumor extent and metastasis status.
- HPV Testing: Especially in young patients, testing for HPV-related tongue cancer may be performed.
Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen ensures rapid and accurate steps in the diagnostic process so treatment can begin without delay.
Stages of Tongue Cancer and Their Importance
Staging tongue cancer is critical for determining the extent of disease and appropriate treatment options. Like other head and neck cancers, tongue cancer is staged using the TNM system.
- Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ): Cancer is confined to the epithelial layer without invasion.
- Stage I: Tumors are less than 2 cm in greatest dimension with no lymph node involvement.
- Stage II: Tumors are 2–4 cm, still localized, with no lymph node involvement.
- Stage III: Tumors larger than 4 cm or spread to ipsilateral cervical lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Tumors invade adjacent structures, contralateral lymph nodes, or distant organs (e.g., lungs).
Accurate staging guides treatment strategy: early-stage disease can often be cured with surgery or radiotherapy alone, while advanced stages require multidisciplinary approaches. Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen creates a tailored treatment plan based on comprehensive staging.
Treatment Options for Tongue Cancer
The goals of tongue cancer treatment are complete tumor eradication, minimal functional loss, and preservation of quality of life. Treatment planning considers tumor stage, patient age, overall health, and personal preferences.
Primary treatment modalities include:
- Surgical intervention
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted biological therapies (especially for HPV-positive tumors)
These modalities may be used alone or in combination.
Surgical Treatment of Tongue Cancer
Surgery is the mainstay for early-stage tongue cancer. The objective is complete removal of the tumor and, if necessary, involved lymph nodes.
Surgical approaches include:
- Partial Glossectomy: Removal of the tumor-bearing segment of the tongue.
- Total or Subtotal Glossectomy: Resection of most or all of the tongue in advanced cases.
- Neck Dissection: Removal of affected lymph nodes when metastasis is present.
- Reconstructive Surgery: Free flap procedures to restore tongue function and appearance after extensive resections.
Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen balances oncologic control with functional and aesthetic outcomes in his surgical planning.
Radiotherapy in Tongue Cancer
Radiotherapy serves as an alternative or adjunct to surgery in tongue cancer management.
Indications include:
- Adjuvant Radiotherapy: Eliminating microscopic disease post-surgery.
- Definitive Radiotherapy: Primary treatment when surgery is contraindicated or declined.
- Neoadjuvant Radiotherapy: Tumor reduction before surgery.
Modern techniques such as IMRT (Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy) allow high-dose delivery to tumors while sparing surrounding healthy tissues. Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen works closely with the oncology team to plan and monitor radiotherapy.
Chemotherapy in Tongue Cancer
Chemotherapy is used concurrently with radiotherapy or as systemic therapy in metastatic disease.
Key uses include:
- Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy: For advanced-stage disease.
- Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Tumor reduction before surgery.
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy: High-risk patients post-surgery.
- Metastatic Disease: To prolong survival.
Regimens are personalized by medical oncologists based on patient condition and tumor biology. Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen collaborates with medical oncology for comprehensive care.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up
Regular follow-up after treatment is vital for early detection of recurrence and maintaining quality of life.
Typical follow-up schedule:
- Every 3 months in the first 2 years with clinical exams and imaging.
- Every 6 months in years 3–5.
- Annually after 5 years.
Follow-up may include oral exams, neck ultrasound, imaging studies, and biopsies if indicated. Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen ensures systematic post-treatment surveillance to reduce recurrence risk and improve long-term outcomes.
Can Early-Stage Tongue Cancer Be Cured?
Yes, early-stage tongue cancer has a high chance of cure with surgery and/or radiotherapy.
How Does HPV Affect Tongue Cancer?
HPV-positive tongue cancers generally respond better to treatment and have higher long-term survival rates.
Does Surgery Affect Speech?
Speech impact depends on tumor size and extent of resection. Reconstructive techniques aim to preserve function.
Does Taste Return After Treatment?
Some patients experience reduced taste sensation, which may partially recover over time. Extensive resections can cause permanent changes.
When Can Normal Eating Resume?
A liquid or puree diet is used initially. Normal diet is resumed as healing progresses, based on individual recovery.
Tongue cancer is a serious disease that can be effectively controlled with early diagnosis and modern treatment. Reducing risk factors, maintaining oral hygiene, and monitoring oral changes are essential in the fight against tongue cancer.
At his private clinic in Istanbul, ENT specialist Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen offers patients the highest success rates in tongue cancer diagnosis and treatment through scientific excellence, multidisciplinary collaboration, and patient-centered care.
If you suspect any abnormality in your tongue health or wish to learn more about tongue cancer, contact Prof. Dr. Ozan Seymen to explore early diagnosis and effective treatment options.










 Türkçe
Türkçe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch